No products in the cart.
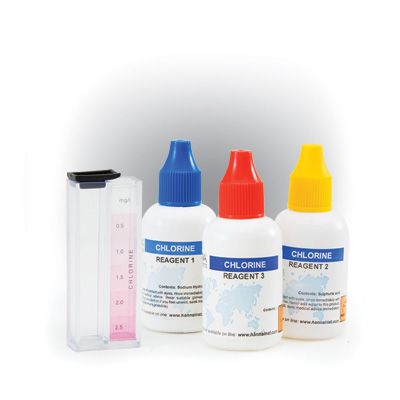
HI3831F CTK Chlorine Free
฿1,284.00
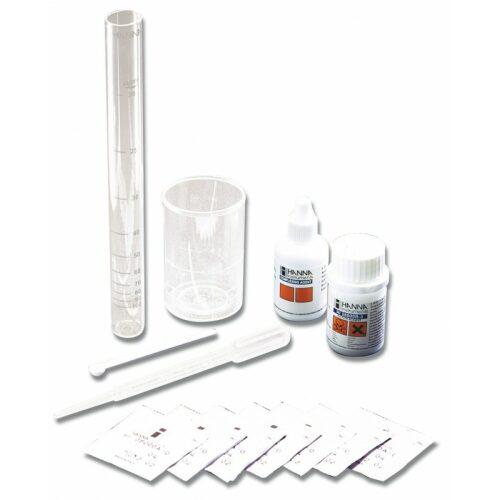
Chemical test kit for the determination of free chlorine in the range 0 to 2.5 mg / l (ppm).
0 in stock
SKU: HI3831F
Categories: All Product, Chemical test kits, Colorimetric
Free chlorine reacts with ammonium ions and organic compounds to form chlorine compounds resulting in diminished disinfecting capabilities compared with free chlorine. These chlorine compounds together with chloramines form combined chlorine. Combined chlorine and excess free chlorine together result in total chlorine. While free chlorine has a much higher disinfectant potential, combined chlorine has a much higher stability and has a lesser volatility. There should be sufficient levels of unreacted free chlorine for adequate disinfection, but not so much as to become harmful.
Order Information:
HI 3831F and HI 3831F/S test kit comes with color comparison cube, 20 mL reagent 1 and 15 mL reagent 2.
Product Manuals
![]() Manual: Download
Manual: Download
| Method | Colorimetric | |
| Range | 0.0-2.5 mg/L | |
| Smallest Increment | 0.5 mg/L | |
| Chemical Method | DPD | |
| Number of Tests | approx. 50 | |
| Weight | 176 g |
Related products
All Product
฿4,494.00
Test kit for the chemical determination of oxygen dissolved in the range 0 to 10.0 mg / l (ppm). 110 tests
All Product
฿7,757.50
Chemical test kit for the determination of free and total chlorine in the range 0.0-0.70/0.0-3.5/0.0-10.0 mg / l (ppm). 200 tests
All Product
฿7,276.00
Test kit for the chemical determination of silicate in the range 0-40mg / l / 0 800 mg / l (ppm). 100 Tests
All Product
฿1,712.00
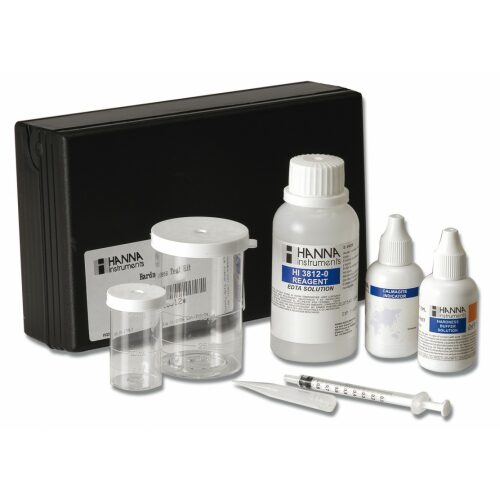
Chemical test kit for the determination of total hardness in the range 0.0 to 30.0 mg / l / 0 to 300 mg / l (ppm). 100 Tests
All Product
฿5,136.00
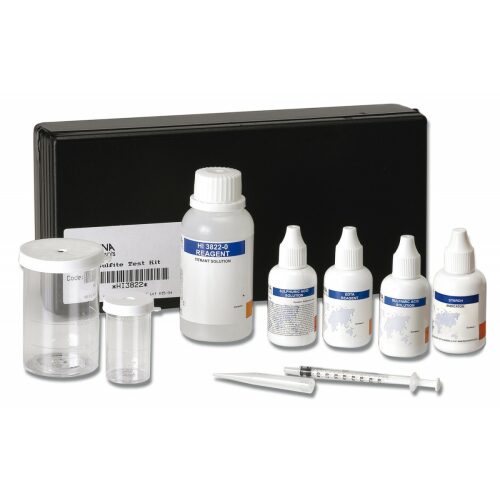
A test kit for the determination of chemical sulphite in the range 0 to 20 mg / l / 0 to 200 mg / l (ppm). 110 tests
All Product
฿2,621.50
Chemical test kit for the determination of chloride in the range 0 to 100 mg / l / 0 to 1000 mg / l (ppm).
All Product
฿4,815.00
Test kit for the chemical determination of sulfate in the range 20 to 100 mg / l (ppm). 100 Tests
All Product
฿642.00
Chemischer Testkit zur Bestimmung der Härte im Bereich 400 bis 3000 mg/l (ppm). Packungsgröse: 50 Tests